Accelerated Carbonation Technology (ACT) is an effective waste treatment process that stabilises contaminants, enhances the handling of the wastes, and can reduce disposal costs.
Waste Treatment
A multitude of wastes can be readily treated and rendered less hazardous using ACT.

- Municipal energy recovery
- Sewage energy recovery
- Biomass energy recovery
- Cement manufacture
- Steel / metal manufacture
- Quarrying / mining
- Bottom ashes
- Boiler ashes
- Fly ashes
- FGTs / APCrs
- Drosses / Slags
- Mineral by-product
The reaction promotes rapid solidification and improved mechanical properties and modification of contaminant mobility.
ACT results in a reduction in porosity due to the formation of voluminous calcium carbonate in the pore space. This aids the retention of contaminants through improved physical containment. Crystals of calcium carbonate join together into an interlocking lattice, forming an unimpaired bond between grains.
The carbonation reaction results in chemical stabilisation which improves contaminant retention. Under optimum conditions the rate of heavy metal release can be reduced by up to several orders of magnitude. This is due to precipitation of metals as low solubility carbonates, the formation of solid solutions in the precipitated calcium carbonate, and sorption onto crystal surfaces.
 solidification
solidification
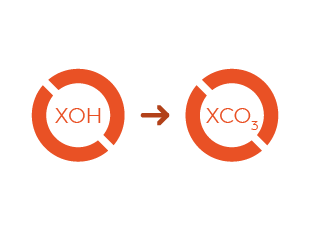 conversion
conversion
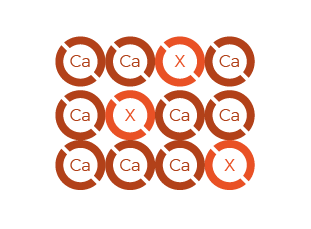 solid solution
solid solution
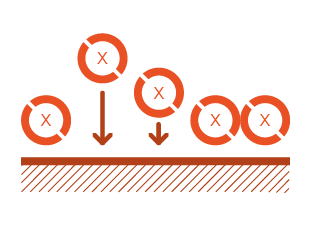 sorption
sorption
ACT can be used to alter the physical properties of the waste to improve handling. Granulation of fine-grained powders, and moisture adjustment can be achieved. Treatment of waste using ACT can facilitate easier end of life management and reduce disposal costs.
Waste treatment using ACT can be used as a step towards valorisation as Sustainable Construction Products.
